
Gradually increase your mileage and intensity (no more than 10% increase in weekly mileage), and practice reducing your pace.
Symptoms: Stiffness and weakness in the muscles of the back of the thigh from the hips to the knees.
Because it controls the trajectory of the knee, strengthening the quadriceps can provide better support for the knee.
It can be strengthened through side walking, side leg lifting, and single leg squat exercises.

Nowadays, running injuries have become a common problem, and many runners are also troubled and unable to run well, even having to say goodbye to the sport of running.
Later, the pain disappears, and after running, you feel severe pain again.
Both deep squats and side squats can be used to stretch the hip flexors.
The best prevention method: (1) Pay attention to the pace.
.
As the condition worsens, pain can occur both inside and outside of the knee, even for a full day.
As the condition worsens, pain can develop up and down the legs, even when walking down stairs or downhill.
The best prevention method: (1) Step by step.
Recommended: Straight Leg Lift Exercise: Lie on your back, straighten one leg, lift it 30 ° to 60 °, and then put it down.
Increase the number of additional rest days, and reduce the amount of running by at least 50% until the pain disappears.
Gradually practice walking 15 steps on each side.
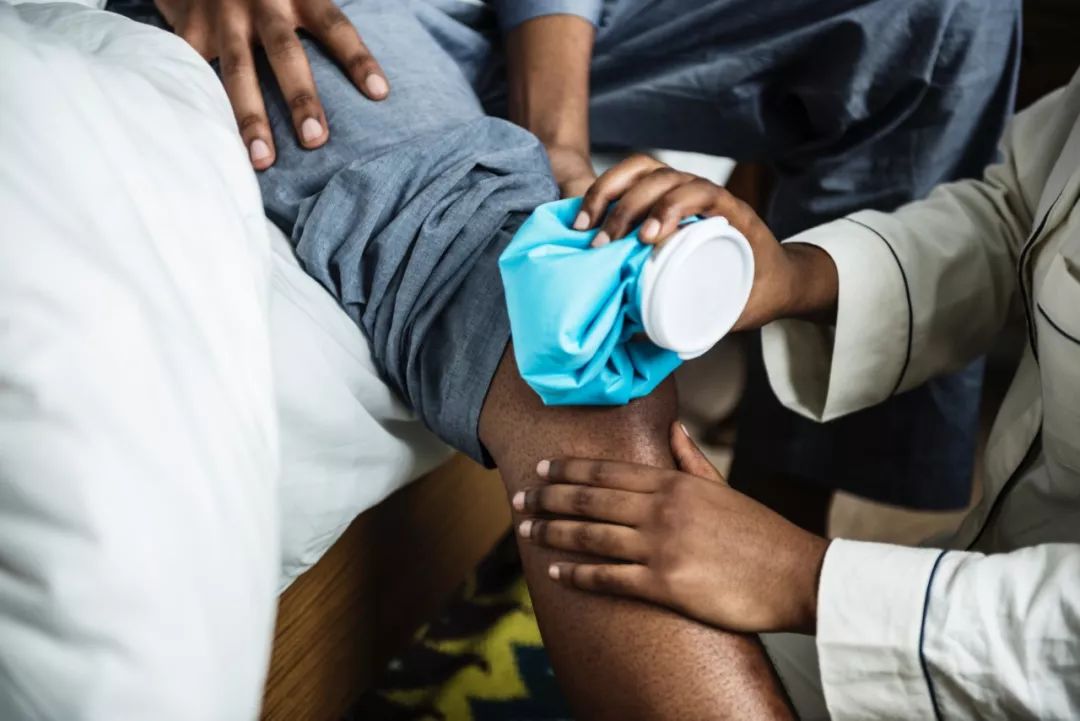

There are many benefits of running, and many runners enthusiasts persist in running with enthusiasm! However, did you know that running can bring health to people, but if you don’t run properly, it can easily cause yourself running injuries.
The best treatment: (1) Reduce the amount of running.
The best treatment: (1) Run easily and reduce your pace.

(3) Reduce your pace and don’t do speed exercises for 3-5 weeks.
Avoid cycling, mountaineering, and putting pressure on the hamstrings.
Symptoms: There is pain in the cartilage below the knee, which can cause severe pain at the beginning of running.
In severe cases, acute pain can occur.
This strengthens core strength and assists the quadriceps.
This also helps to correct excessive varus.
During initial practice, you can do 5 groups at a time, gradually practicing to 10 groups.
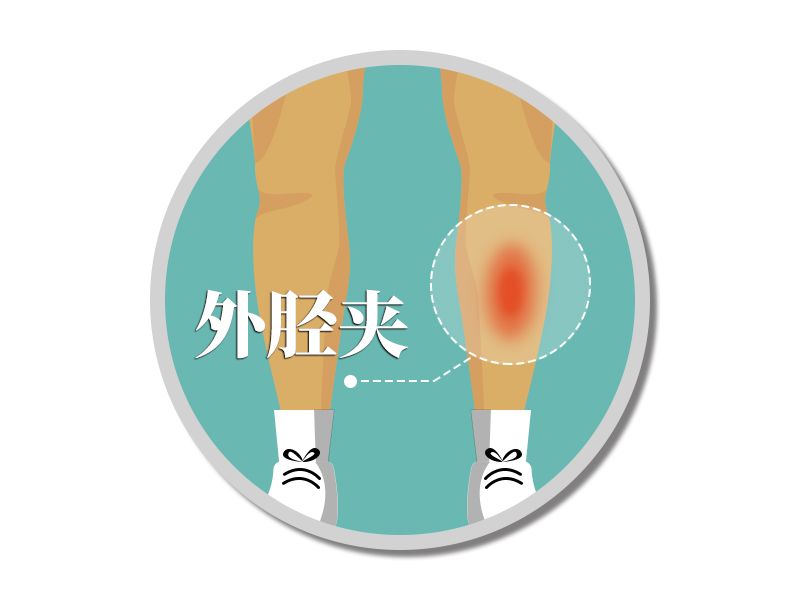
The iliotibial tract is the connective tissue that connects the hip and tibia on the outside of the thigh, extending from the hip to the knee.
During running, as the knees bend and extend, the iliotibial band rubs against the thigh bones, resulting in excessive friction and inflammation.
Once you have signs of pain, take a day or two off, switch to a light run, and then halve your mileage for a week or so.
The hamstrings are located at the back of the thigh and rely on these muscles to bend the knee, stretch the leg, climb hills, and shoot goals.
During an injury, elliptical machine training, swimming, or water running can be used as an alternative to training.
Prevention methods: (1) Strengthen quadriceps exercise.
The reason for the strain is that the legs open too much during acceleration, which is called excessive stride.
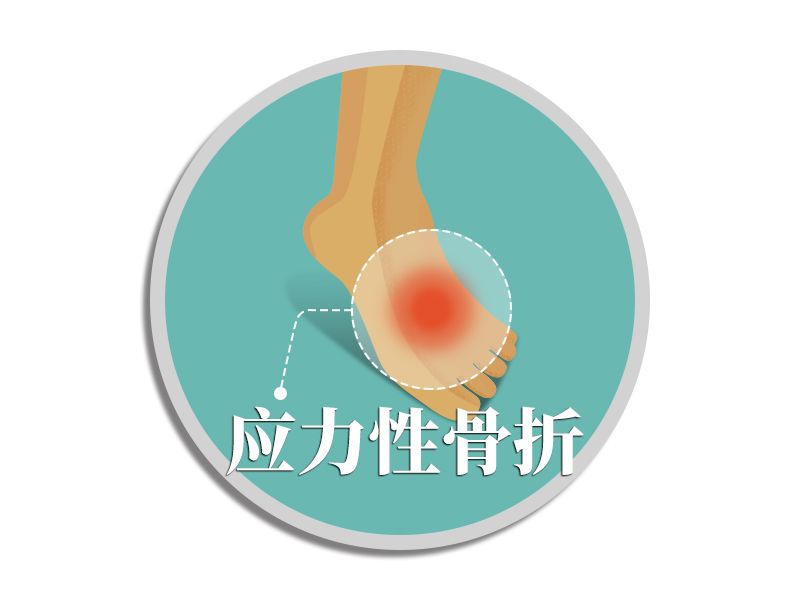
Reason: Increasing the amount of running too fast, too much, or running too much on arched roads (such as downhills).
Swimming, water running, and elliptical machine training are all good training methods.

(2) When the thigh hurts, avoid stretching the area to prevent another strain.
Cause: There are many reasons for hamstring strain, including excessive walking or excessive forward leaning above the waist, excessive speed training, and even too fast or excessive mountain training.
Also known as “patellar joint syndrome”, it refers to pain under the patella, which is the main cause of knee pain, usually occurring after long-distance running, running, or when walking down the stairs or lower limbs.
Problems with the hamstring muscle are usually caused by weak muscles.
Simply put, it is caused by too much pressure on the knees, or by long-distance running, or sitting for a long time, or by carrying a load downhill or down the stairs.
Do this quickly for 10 times, and then switch to the other leg.
Avoid walking and cycling to prevent further injury to the iliotibial tract.
(2) Massage with foam shaft.
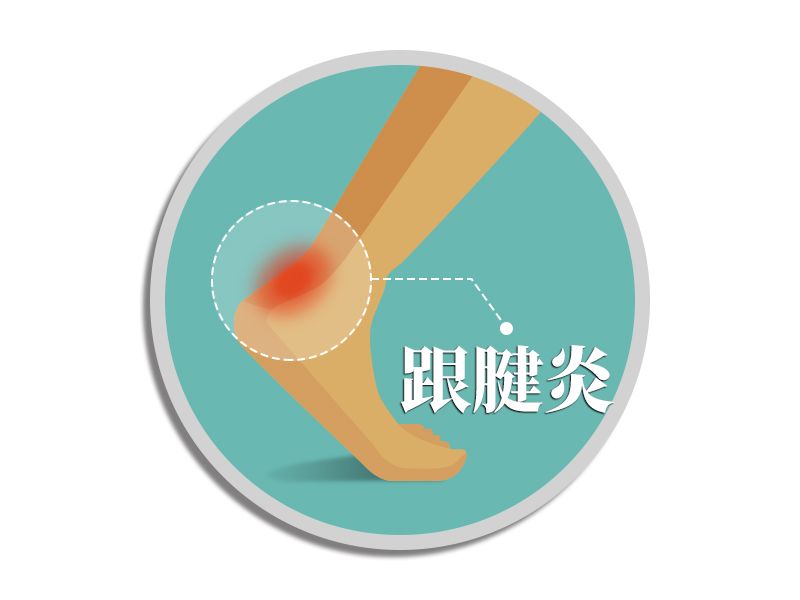
(4) Alternate training, such as swimming or elliptical machine training.
With the help of the foam shaft, you can lie on it obliquely, and then roll up and down between the knee and hip, which can stimulate blood flow to this area, and also relax the strained iliotibial band, reducing pain.
The best treatment: (1) Reduce the amount of running.
Symptoms: Slight pain on the outside of the knee, usually starting in the first few kilometers of running.
Recommended Practice: Sidewalk: Wrap your legs under your knees with a strap; Take 10 steps to the right in a squat position, then 10 steps to the left.
“You feel pain and muscle tightness for a long time, and you have to slow down and slow down your pace.”.
(2) Strengthen the abductor muscles of the buttocks.
Avoid running downhill or leaning forward excessively, as this will put more pressure on the knees.
Whether it’s preventing them before they occur or recovering from them, it’s always beneficial to learn more.
Stand with your left foot crossed in front of your right foot; Bend your upper body to the left and raise your hands above your head; Keep your knees straight, bend your upper body as much as possible, and hold for 15-20 seconds; Then switch legs and repeat on the other side.
Increasing your mileage too fast, or running downhill too fast, can cause strain.
Cause: weakness in the quadriceps, buttocks, or gluteus maximus can all lead to excessive varus (excessive inward rotation of the foot) and poor knee movement trajectory.
This is caused by injury to the iliotibial tract.
(3) Cross training.
Today, let’s take a look at the seven common types of running injuries.
Repeat for 3 groups, 10 times for each leg in each group.
(2) Strengthen hip muscle exercises.
In people with iliotibial tract syndrome, the abductor muscles of the buttocks are generally weak because the muscles connected to the iliotibial tract have to replace the weak gluteus muscles to function, while also helping to maintain the level of the buttocks, resulting in excessive workload and pressure on the iliotibial tract.
Do each of the two legs 10 times as a group.
Excessive forward leaning during running can also affect the knees.
(4) Alternative training.

Single Leg Squat: Stand on one leg, with the toes of the other foot pointing forward; Move your weight to the forefoot of the standing leg and lower into a squat position.
(2) Avoid going downhill.
If the iliotibial tract is injured, recovery is slower.
(3) Standing and side stretching exercises.
