Therefore, injuries can be prevented by exercising the strength of these muscles (such as quadriceps femoris, hamstring and gastrocnemius).
Hamstring knee flexion is mainly the result of hamstring contraction.
In addition to the quadriceps and hamstrings, there are other important muscles around the knee, which are responsible for completing various knee movements and maintaining joint stability.
The main function of the gastrocnemius at the back of the knee is to straighten the foot (plantar flexion).
The meniscus can also help maintain the stability of the knee.
Without the meniscus, the tibia and femur rub against each other, causing rapid bone wear.
When it comes to where is the most vulnerable to injury, the knee is naturally the first part most people think of.
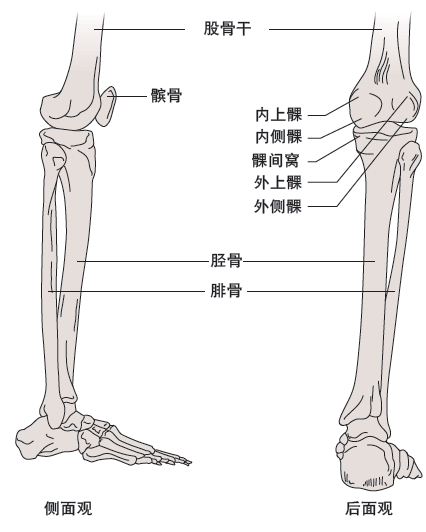
The main movement of knee joint is completed by the joint formed by tibia and femur, which is also called tibiofemoral joint.
There are four main ligaments in the knee joint.

Hamstring is the general name of biceps femoris, Semimembranous muscle and semitendinosus muscle.
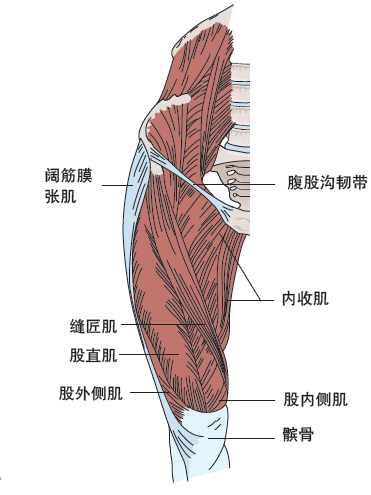
The muscle starts near the groin and its main function is to adduct the femur.
The above content comes from the guide to sports protection: prevention, evaluation and recovery of sports injury (3rd Edition) introduced and published by the people’s Posts and Telecommunications Publishing House -.
Cartilage the ends of the tibia and femur are covered with tough cartilage called the meniscus, which has a cushioning effect.
Iliotibial tract is a tough connective tissue.
Even some people want to understand the structural characteristics of the knee after repeated injuries.
At the same time, the gastrocnemius also flexes the knee joint together with the hamstring muscle.
The anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments pass through the middle of the knee joint and cross each other, so “cross” means “cross”.
Anterior cruciate ligament Ligament (ACL) limits the excessive forward movement of the tibia relative to the femur, The posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) prevents excessive posterior displacement of the tibia relative to the femur.
The location of the hamstring attachment point helps limit excessive forward movement of the tibia relative to the femur.

The iliotibial tract is located outside the knee.
Muscle the muscles of the knee can not only produce joint activity, but also maintain the stability of the joint.
The main muscles of the knee joint include quadriceps femoris and hamstring.
In fact, understanding the structure of the knee is helpful to judge the location and type of injuries, so that you can better deal with injuries.
Quadriceps femoris stretching knee joint is mainly completed by quadriceps femoris, which is composed of medial femoral muscle, lateral femoral muscle, medial femoral muscle and rectus femoris muscle.
The gracilis muscle is located inside the knee.
Tibial collateral ligament Ligament (MCL) helps maintain the stability of the medial knee, The fibular collateral ligament (LCL) helps maintain the stability of the lateral knee.
The bones that make up the knee joint include the femur, tibia, and patella.
Let’s learn about the structure of the lower knee ~ in short, the knee joint is composed of 3 bones, 2 main muscles, 4 main ligaments and cartilage to maintain joint stability.
How to prevent knee injury? According to the above analysis, the muscles of the knee can maintain joint stability and help limit abnormal bone movement.
If you run more, you will have more or less injuries.
However, many runners know little about the knee before they are injured, so that they do not pay enough attention after injury.